TOLL FREE:
1-866-611-2665
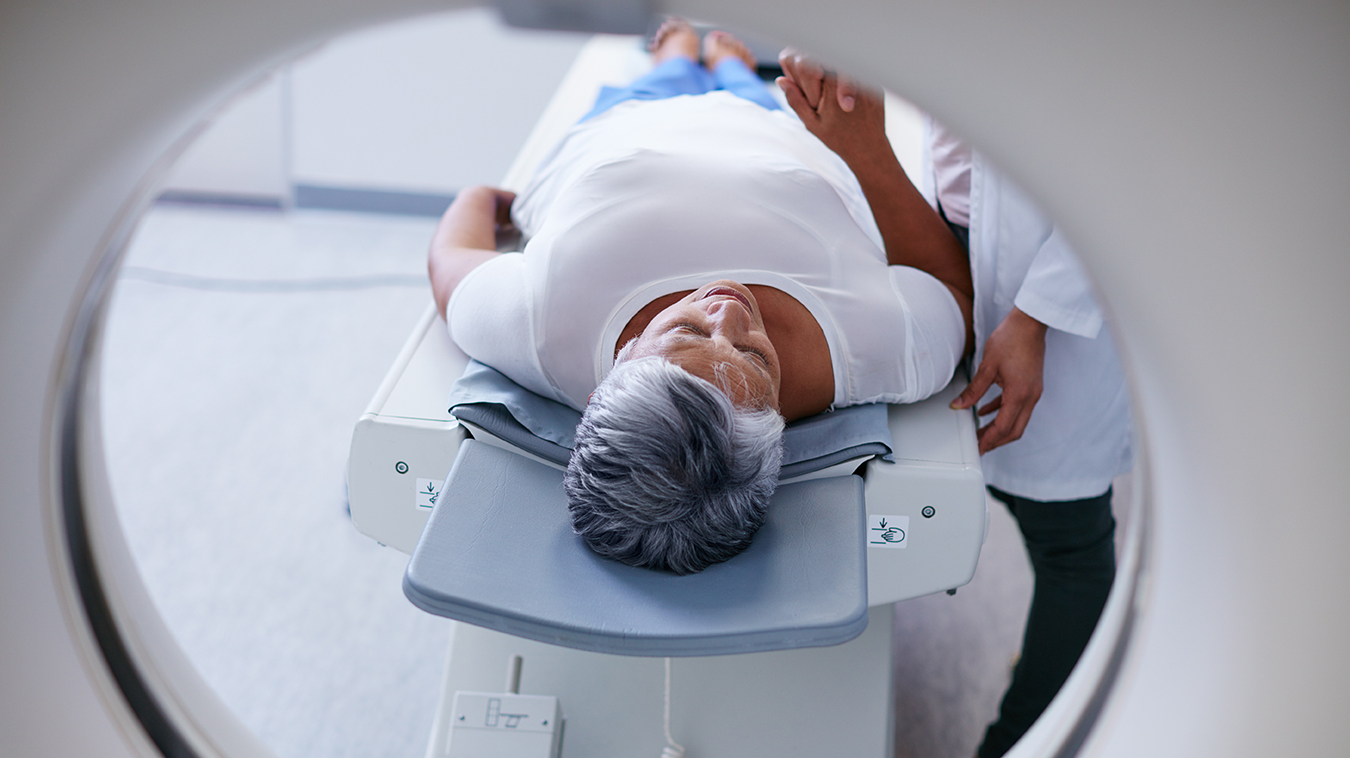
Home WHAT IS CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY?
Coronary arteries deliver blood to the heart, so anything that affects their function can have serious health implications. If the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle is impeded as a result of coronary artery disease (CAD), this can lead to heart failure and possibly a heart attack.
The most common cause of CAD is a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery causing it to narrow or become blocked – also called atherosclerosis. These coronary arteries are small – often just three or four millimetres wide – putting them at risk with any buildup. Plaque can be composed of various substances that circulate in your blood, including calcium, fat, and cholesterol. Plaque buildup can start at an early age and is cause by a combination of genetic and lifestyle risk factors.
For those at risk of CAD, a coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can be used to non-invasively examine the coronary arteries. Using a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce comprehensive, detailed images, CCTA can detect both calcified or hard plaques and noncalcified or soft plaques. It is these soft plaque deposits, often invisible with standard imaging tools, that are more likely to cause heart attack related health issues.
The night before your CCTA exam (and sometimes again shortly before the exam) you will need to take beta blockers to lower your heart rate. A nurse will also monitor your blood pressure and heart rate and start an intravenous (IV) line for the CT contrast solution. Once the exam begins it’s very similar to an X-ray. You will be positioned on a table while the technologist adjusts the scanner. The technologist then leaves the room, and the scan begins. At different times throughout your exam, you will be asked to hold your breath for about 10-15 seconds.
Your exam will measure the amount of calcium deposits surrounding your coronary arteries and assess the lumen of the coronary arteries for any narrowing. It will also assess the wall of the coronary vessels for any soft plaques. The process is painless and usually takes between 15-20 minutes. However, the appointment can last from one to two hours depending on how well the beta blockers work to lower your heart rate. If your heart rate is too high, it’s difficult to obtain clear pictures of your coronary arteries.
After your scan, we will remove your IV and escort you to our waiting lounge for about 20 minutes to make sure you are feeling well and drinking plenty of fluids, and to check your blood pressure and heart rate. Your images will be interpreted by one of our radiologists and a report will be sent to your doctor within the same business day, or by the next business day at the latest.
At Mayfair Diagnostics CCTA screening is only available as a private pay exam, not covered by the Alberta Health Insurance Plan. Mayfair Diagnostics offers community-based private CT services as a complement to the public health care system.
Through the public health care system, CCTA has some, but limited availability. A traditional angiography may also be offered. During this procedure, a thin, hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery (usually in the arm or leg) and threaded up into the heart. A contrast dye is then injected through the catheter to document areas of coronary artery narrowing. The benefits of this procedure are that it can be used for both diagnosis and treatment in a single session. However, it’s invasive, requires fasting before the procedure, and in-hospital recuperation afterward.
Whether public or private, a traditional angiography and a CCTA must be requested by a health care practitioner. To determine what is recommended, patients and their doctors often review medical and family history, risk factors, and if there are symptoms, how long symptoms have been present and how they affect daily activities. If a private CCTA scan is indicated as a best next course of action for a patient, a requisition will be provided and the appointment can be booked.
Not all patients are good candidates for this exam. It’s also important to note that the exposure to radiation from a CCTA scan is higher than that of standard X-rays, but the associated risk is still small. For example, the radiation exposure from one CCTA is around the exposure from the earth’s natural background radiation in one year. In most cases, the benefits of a CCTA, such as the early detection of a serious illness, significantly outweigh the small increased risk from radiation exposure. CCTA also has the small possible risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast dye.
For more information on CCTA, please visit the exam page.
REFERENCES
Doh, J. H., et al. (2014) “Diagnostic value of Coronary CT angiography in comparison with invasive Coronary angiography and intravascular ultrasound in patients with intermediate Coronary artery stenosis: results from the prospective multi-centre FIGURE-OUT (Functional Imaging criteria for GUiding REview of invasive Coronary angiOgraphy, intravascular Ultrasound, and Coronary computed Tomographic angiography) study.” European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging. August, 15(8): 870-7. Accessed October 18, 2022.
Government of Alberta (2022) “Computed Tomography Angiogram (CT Angiogram).” www.myhealth.alberta.ca. Accessed October 18, 2022.
Government of Alberta (2022) “Coronary Artery Disease: Should I Have an Angiogram?” www.myhealth.alberta.ca. Accessed October 18, 2022.
Johns Hopkins Medicine (2022) “Anatomy and Function of the Coronary Arteries.” www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Accessed October 18, 2022.
University of Ottawa Heart Institute (2022) “Coronary Artery Disease (Atherosclerosis).” www.ottawaheart.ca. Accessed October 18, 2022.
Our Refresh newsletter delivers the latest medical news, expert insights, and practical tips straight to your inbox, empowering you with knowledge to enhance patient care and stay informed.
By subscribing to our newsletter you understand and accept that we may share your information with vendors or other third parties who perform services on our behalf. The personal information collected may be stored, processed, and transferred to a country or region outside of Quebec.
Please read our privacy policy for more details.