
Home TREATMENT FOR AN ENLARGED PROSTATE
Over 30% of men aged 50 and over require treatment for an enlarged prostate and for some of them that means surgery.
The prostate gland sits underneath the bladder and surrounds part of the urethra, the tube that carries urine and semen out of your penis. Normally, it’s the size and shape of a walnut, but as men age it can sometimes get too big and start to squeeze the urethra. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It can disturb sleep with frequent urination overnight, cause a hard time urinating, or a weak stream when you do start.
It’s a common condition with a number of treatment options, ranging from lifestyle changes to medication to surgery. Your health care practitioner can help you determine the best option for you based on your age, health, and current symptoms.
In cases of surgery, the most commonly performed procedure is a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Very large prostates are not effectively treated with TURP, so an open surgery is usually performed to completely or partially remove the enlarged prostate. These are not the only options, however. Mayfair Diagnostics radiologists have been successfully performing prostate artery embolization (PAE) procedures as an alternative to surgery in Calgary hospitals since 2012.
First performed in 2009 by Professor Pisco in Portugal, this procedure shrinks an enlarged prostate by non-surgically blocking the arteries that feed the gland. An interventional radiologist, rather than a surgeon, performs the procedure through a pinhole in the groin.
The interventional radiologist will use X-ray guidance to painlessly move a small plastic tube through a tiny hole in the skin around the blood vessels of the body into the small arteries which are feeding the prostate. A special X-ray dye is injected down the catheter to identify the prostate blood supply. After navigating the tube, small metal coils or glue-like liquids can be injected through the tube into these small arteries to block them and starve the prostate of its blood supply.
PAE is done using a local anesthetic in the groin and intravenous painkillers and/or sedatives, if needed. A catheter is inserted into the bladder for a few hours during the procedure.
During a TURP, an instrument is inserted into the tip of your penis and extended through your urethra into the prostate area. Your doctor will then use it to trim tissue from the inside of your prostate gland, one small piece at a time, to remove the section of the prostate that is blocking urine flow. As small pieces of tissue are removed, irrigating fluid carries them into your bladder.
TURP is done using a general or spinal anesthetic and a catheter will be inserted into your bladder. It usually requires a one- or two-day stay in the hospital and the catheter is generally left in place for 24-48 hours, until the bleeding subsides.
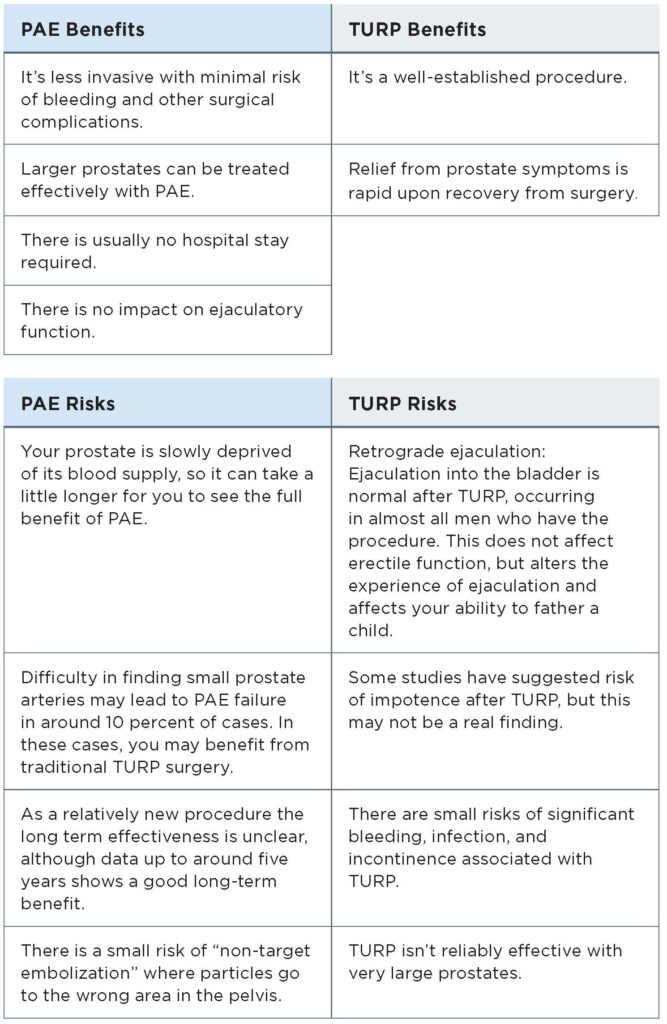
**SPECIAL NOTE: TURP is not effective for patients who have a very large prostate (3 times normal size), so they are usually sent for open prostatectomy – the prostate is removed through an incision above the pubic bone. This carries the usual surgical risks, especially for patients in their 70s and 80s who commonly have this problem combined with other health issues. There is also a risk of incontinence. A pinhole surgery without general anesthetic, such as PAE, would be more effective for these patients as well.
Mayfair Diagnostics interventional radiologists perform these embolization procedures in-hospital within Calgary. These procedures are covered under the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Out-of-province patients are accepted; you would need to confirm with your provincial health care plan that they will cover the procedure as Alberta Health Services (AHS) will bill your provincial plan.
If you think you might benefit from this procedure, you will need to speak with your family doctor or specialist. Your doctor or specialist will then need to fax a consultation request to Rockyview General Hospital’s Diagnostic Imaging department at 403-592-4852.
Once the information has been received, our interventional radiology team will review the request and contact you to arrange a consultation to determine if the procedure is appropriate based on your medical history. There may also be imaging required. For example, a CT scan of the prostate may be ordered.
For more information, please contact the Mayfair Diagnostics Customer Contact Centre via the following options:
REFERENCES
Bandukwala, N. Q. (2020) “What is BPH?” www.webmd.com. Accessed June 2, 2022.
Elterman, D., et al. (2022) “UPDATE – 2022 Canadian Urological Association guideline on male lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia (MLUTS/BPH).” Canadian Urological Association Journal, April 11. Accessed June 2, 2022.
Gao, Y., et al. (2014) “Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Prostatic Arterial Embolization versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate—A Prospective, Randomized, and Controlled Clinical Trial.” Radiology, Mar; 270 (3): 920-28. Accessed June 2, 2022.
Healthwise Staff (2021) “Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.” www.myhealth.alberta.ca. Accessed June 2, 2022.
Kapoor, Anil (2012) “Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) management in the primary care setting.” The Canadian Journal of Urology, Oct. 19(1): 10-17. Accessed June 2, 2022.
Mayo Clinic Staff (2022) “Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).” www.mayoclinic.org. Accessed June 2, 2022.
We foster a supportive and collaborative culture designed to encourage positive patient experiences and build strong working relationships across the organization:
Our core values shape the way we work with patients, partners, and fellow employees. And, more than anything else, they’re what set Mayfair apart. In everything we do, this is what we strive for:
EXCELLENCE
We share a commitment to high quality and excellence in all that we do. This commitment calls on all of us to achieve the very best of our capabilities and exceed our own expectations.
CURIOSITY
We innovate in everything, from services to processes. We believe meaningful change and effective problem solving come only by looking at challenges and opportunities from new angles and by exercising our creativity and curiosity.
PASSION
We show pride, enthusiasm, and dedication in everything that we do. We are committed to producing and delivering high-quality results and services. We are passionate about our industry and about our company, services, partners, and patients.
COLLABORATION
Our team is supportive of each other’s efforts; we are loyal to one another; and we care for one another both personally and professionally. We promote and support a diverse, yet unified, team. We work together to meet our common goals across Mayfair clinics, locations, and geographies. Only through collaboration on ideas, technologies, and talents can we achieve our mission and vision.
SERVICE
We take pride in delivering exceptional service every day. We listen to every request with an open mind, always looking for opportunities to go above and beyond to create memorable, personalized experiences. We take responsibility to answer our referrers’ and patients’ requests and respect their time by always responding with a sense of urgency.
Start a career with Mayfair Diagnostics — one of Western Canada’s leading medical imaging teams.
Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, we’ve been helping people f ind clarity for their health for over 100 years. At our clinics in Calgary and area, Regina, and Saskatoon, our team of radiologists, technologists, and support staff work in a truly integrated way to provide exceptional experiences for our patients. Joining our team is more than a job. It’s an investment in your future — a plan for success.
OUR PEOPLE
Our people share our quest to make a difference in our patient’s lives. We’re a team of professionals, disciplined in our skills and compassionate with our patients, providing the care and attention they need. At our core, we are a trusted partner in our patients’ health care journey. Our patients, physicians, and other health care providers rely on us for quality imaging to help manage their patient’s health care decisions with certainty. But our business is about more than just imaging. It’s about building lasting relationships and making a meaningful difference in the lives of those we meet.
OUR VISION
A world in which every person has clarity about their health. We push the boundaries of what is possible and embrace change as an opportunity. We strive to be thought leaders and encourage creativity by providing a safe place for calculated risk taking. We learn from our mistakes. We share best practices across our operations and are recognized by our peers for our work. We engage the best to help propel us forward in achieving our goals.